Menu
Metal complex dyes are premetallised dyes that show great affinity towards protein fibers. In this dye one or two dye molecules are coordinated with a metal ion. The dye molecule is typically a monoazo structure containing additional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl or amino, which are capable of forming a strong co-ordination complexes with transition metal ions such as chromium, cobalt, nickel and copper.
Metal-complex dyes belong to numerous application classes of dyes. For example, they are found among direct, acid, and reactive dyes. When applied in the dyeing processes, metal-complex dyes are used in pH conditions that are regulated by user class and the type of fiber type (wool, polyamide, etc). The pH levels for wool typically range from:
Types of Metal Complex Dyes
The classification of metal complex dyes is dyes is based on the basis of number of dye molecules which are complexed with one metal ion
1:1 metal complex dyes: In 1:1 metal complex dyes one metal ion is complexed with one dye molecule.
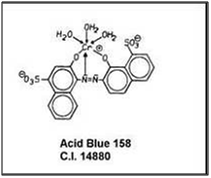
2:1 metal complex dyes: In 2:1 metal complex dyes there are two dye molecules which are complexed with one metal atom.
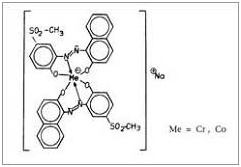
Features of Metal Complex Dyes
Application of Metal Complex Dyes
Metal Complex Dyes is using for a variety of applications like wood stains, leather finishing, stationery printing inks, inks, coloring for metals, plastic etc. As this dye is classified into two categories and both have different applications.
1:1 metal complex dyes:
These dyes have good leveling and penetration properties and are particularly suitable for application on carbonized wool. These dyes are applied under a strongly acidic bath at a pH of 1.8 –2.5 with sulfuric acid or at a pH of 3-4 with formic acid, therefore these are not suitable for the blends having cotton component. Glauber salt is used as exhausting agent and organic leveling agents are used too.
2:1 metal complex dyes:
These dyes are subdivided into two subgroups based on the solubilising groups present in the dye molecule, these dyes shows moderate migration properties on nylon but very good overall fastness properties, because metal complex dyes not only attach to nylon with ionic linkages, but also with coordinate bonds. The two subgroups are: